What Are Some Essential Metals?
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Essential Metals
- Common Essential Metals and Their Uses
- Properties That Make Metals Essential
- Industrial Applications of Essential Metals
- ORO Mineral’s Role in Metal Processing
- Environmental Considerations in Metal Mining
- Future Trends in Essential Metals
- Summary Table of Key Takeaways
- FAQs
- References
Introduction to Essential Metals

Metals play a critical role in modern society, serving as building blocks for technology, infrastructure, transportation, and energy. Understanding which metals are considered essential can help industries, investors, and policymakers make informed decisions. In this guide, we explore the most important metals, their properties, uses, and processing methods.
Definition of Essential Metals
Essential metals are metals that are crucial for industrial, technological, or economic purposes. They typically possess properties like high conductivity, corrosion resistance, strength, and malleability. These metals are often required in large volumes for applications that support modern life, including electronics, transportation, and construction.
Common Essential Metals and Their Uses
1. Copper (Cu)
- High electrical and thermal conductivity.
- Used in electrical wiring, motors, and renewable energy technologies.
- Also found in plumbing and architectural applications.
2. Aluminum (Al)

- Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and durable.
- Used in aircraft, transportation, packaging, and construction.
3. Iron (Fe) & Steel

- Core structural material for buildings and infrastructure.
- Steel, an alloy of iron and carbon, is versatile and widely used.
4. Zinc (Zn)
- Corrosion-resistant, often used for galvanization.
- Supports battery production and alloys.
5. Nickel (Ni)
- Corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant.
- Used in stainless steel, batteries, and aerospace components.
6. Lead (Pb)
- High density and chemical resistance.
- Used in batteries, radiation shielding, and construction materials.
7. Precious Metals: Gold (Au) & Silver (Ag)
- High conductivity and resistance to corrosion.
- Used in electronics, jewelry, and investment markets.
Properties That Make Metals Essential
- Electrical conductivity: Necessary for wires and electronic components.
- Thermal conductivity: Important for heat exchangers and engines.
- Corrosion resistance: Ensures longevity in harsh environments.
- Strength and durability: Suitable for construction and heavy machinery.
- Recyclability: Promotes sustainable industrial use.
Industrial Applications of Essential Metals
Electronics and Electrical Industry
- Copper for wiring and circuit boards.
- Gold and silver for connectors and microchips.
Construction and Infrastructure
- Steel and aluminum for structural frameworks.
- Zinc for protective coatings.
Transportation and Aerospace
- Aluminum for aircraft and lightweight vehicles.
- Nickel alloys in engines and turbines.
Energy and Renewable Technologies
- Copper in solar panels and wind turbines.
- Nickel in lithium-ion batteries.
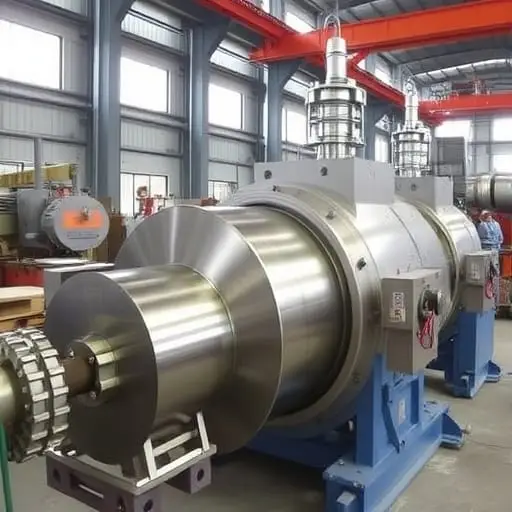
ORO Mineral’s Role in Metal Processing

ORO Mineral is a large-scale intelligent mineral processing equipment manufacturer, integrating research and development, production, and sales. Since 2014, they have contributed to the recovery, separation, and beneficiation of metals, providing high-performance equipment for efficient processing.
Key Products and Their Applications
- Sand Washing Machine 100 TPH Long Life: Cleans raw ores to prepare them for processing.
- Gravity Spiral Concentrator: Separates valuable metals based on density differences.
- 1.1kw Belt Magnetic Separator: Removes magnetic impurities from ores.
- Eddy Current Separator Machine: Separates non-ferrous metals from mixed materials.
- Gravity Spiral Chute Separator: Efficiently segregates heavy metals during beneficiation.
Environmental Considerations in Metal Mining
- Responsible tailings management to prevent soil and water contamination.
- Recycling of metals to reduce environmental impact.
- Energy-efficient machinery to lower carbon emissions.
- Rehabilitation of mining sites post-extraction.
Future Trends in Essential Metals
- Increasing demand for metals in renewable energy and electric vehicles.
- Development of sustainable and eco-friendly mining technologies.
- Advances in metal recycling and recovery processes.
- Automation and AI integration in mineral processing equipment.
Summary Table of Key Takeaways
| Metal | Key Properties | Main Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Copper | Conductive, ductile | Electrical wiring, electronics, renewable energy |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Transportation, construction, packaging |
| Iron/Steel | Strong, durable | Buildings, infrastructure, machinery |
| Nickel | Heat-resistant, corrosion-resistant | Batteries, alloys, aerospace |
| Zinc | Corrosion-resistant | Galvanization, batteries, alloys |
| Gold/Silver | Conductive, non-corrosive | Electronics, jewelry, investment |
FAQs
1. What are essential metals?
Essential metals are metals that are critical for industrial, technological, or economic use due to their unique properties and high demand.
2. Which metals are most important for electronics?
Copper, gold, silver, and aluminum are widely used due to their excellent conductivity and reliability.
3. How does ORO Mineral support metal processing?
ORO Mineral manufactures mineral processing, screening, and separation equipment that improve recovery rates and processing efficiency.
4. Why is recycling essential for metals?
Recycling reduces the environmental impact of mining and ensures sustainable supply of high-demand metals.
5. What metals are expected to see increased demand?
Copper, nickel, lithium, and aluminum are in growing demand due to renewable energy technologies and electric vehicles.
References






