The Complete Guide to the Copper Refining Process (2025 Edition)
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Copper Refining
- Why Copper Refining is Essential
- Main Stages of the Copper Refining Process
- Refining Methods: Pyrometallurgical vs. Hydrometallurgical
- Key Equipment Used in Copper Refining
- ORO Mineral Co., Ltd. — Trusted Partner in Mineral Processing
- Summary Table: Copper Refining Process Overview
- FAQs
- References
Introduction to Copper Refining

Copper refining is a critical industrial process that transforms impure copper extracted from ores into high-purity copper metal. The refined copper serves as a vital component for a variety of industries including electronics, construction, energy, and transportation. High-quality copper ensures superior electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength — key factors that make it indispensable for modern technology and infrastructure.
Since ancient times, copper has been one of the most valuable metals due to its malleability and durability. Today, technological advancements have made refining more efficient, sustainable, and environmentally friendly.
Why Copper Refining is Essential
The refining process removes impurities such as iron, sulfur, gold, silver, and other trace metals from raw copper. These impurities can negatively affect the performance of copper products if not properly removed. The end goal is to achieve copper purity levels above 99.99%, suitable for electrical and industrial applications.
Key Benefits of Copper Refining
- Improved Conductivity: Pure copper ensures maximum electrical efficiency for wiring and components.
- Enhanced Durability: Impurity-free copper resists oxidation and corrosion, extending lifespan.
- Environmental Responsibility: Modern refining processes recycle waste and reduce emissions.
- Economic Value: Refined copper commands a significantly higher market price.
Main Stages of the Copper Refining Process
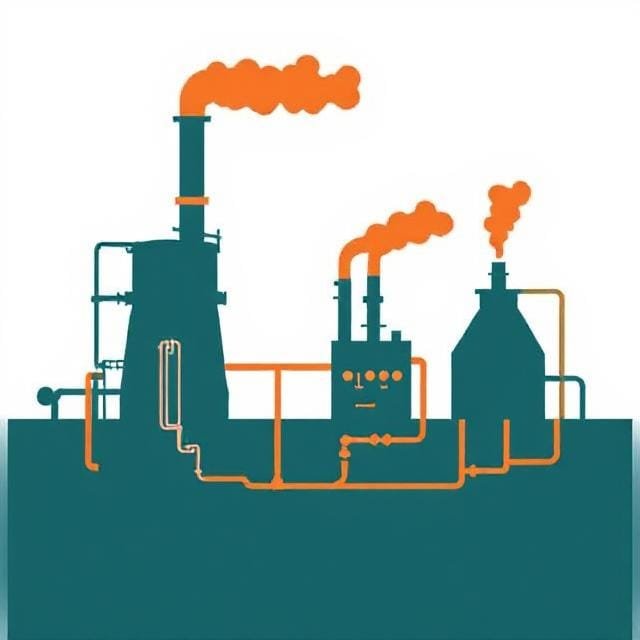

The copper refining process involves multiple stages, from extraction and concentration to smelting and electrorefining. Each stage is carefully designed to increase purity and minimize material loss.
1. Mining and Concentration
The first step involves mining copper ores such as chalcopyrite, bornite, and malachite. These ores are then crushed, ground, and processed using flotation techniques to produce a copper concentrate containing 20–30% copper.
2. Smelting
In the smelting stage, copper concentrate is heated in a furnace at temperatures exceeding 1200°C. The process separates copper from sulfur and iron, resulting in a molten mixture known as matte, which contains about 60–70% copper.
3. Converting
The matte is then transferred to a converter furnace, where air or oxygen is blown through the molten material. This oxidizes the remaining impurities, leaving behind blister copper — named for its blistered surface caused by escaping gases — with a purity of approximately 98–99%.
4. Fire Refining
Fire refining further purifies the blister copper by heating and introducing oxidizing and reducing agents to eliminate residual impurities. The resulting anode copper is cast into large plates for the next step — electrorefining.
5. Electrolytic Refining
In this final stage, the anode copper is dissolved in an acidic copper sulfate solution. An electric current is applied, causing pure copper to deposit onto cathodes, while impurities either fall to the bottom as anode slime or remain in solution.
The electrolytic refining process produces 99.99% pure copper ready for commercial use in wires, circuits, and other applications.
Refining Methods: Pyrometallurgical vs. Hydrometallurgical
There are two primary copper refining methods used in modern industries: pyrometallurgical and hydrometallurgical processes. Both methods have their advantages, depending on the type of copper ore and desired output.
Pyrometallurgical Refining
This traditional method uses high-temperature furnaces to extract and refine copper. It’s mainly used for sulfide ores and involves steps such as smelting, converting, and fire refining.
- High recovery rates for large-scale operations
- Efficient for high-grade ores
- Generates by-products like sulfur dioxide for industrial reuse
Hydrometallurgical Refining
This process is more eco-friendly and suitable for low-grade or oxide ores. It involves leaching copper from ore using acid solutions, followed by solvent extraction and electrowinning (SX-EW).
- Lower energy consumption compared to pyrometallurgy
- Minimal air pollution
- Efficient for small-scale and low-grade operations
Many modern plants use a hybrid approach that combines both methods for maximum efficiency and sustainability.
Key Equipment Used in Copper Refining
Efficient copper refining depends on advanced processing and separation equipment that ensures consistent product quality. Here are some of the most important types of equipment used in this industry.
1. Dry Electromagnetic Separator
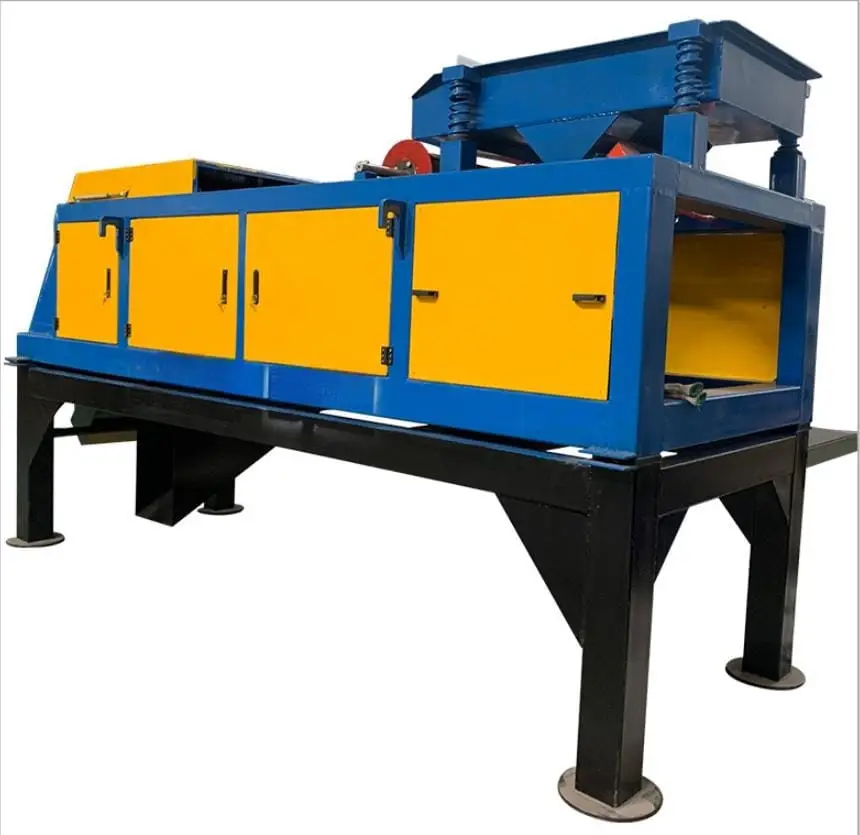

The Dry Electromagnetic Separator is designed to remove magnetic impurities from crushed ore before refining. It enhances ore purity and improves recovery rates.
- High magnetic intensity and stability
- Energy-efficient and dust-free design
- Ideal for pre-refining and mineral separation
2. Gravity Spiral Chute Separator
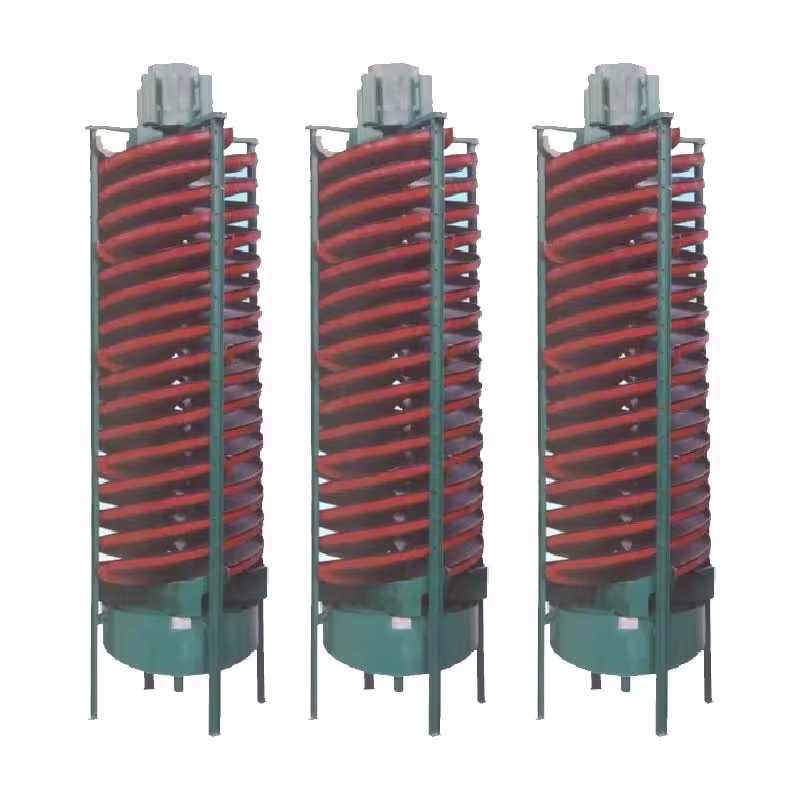

The Gravity Spiral Chute Separator is used for separating fine minerals based on density differences. It’s a critical tool for pre-concentration before smelting.
- Simple structure with high recovery efficiency
- Low operating cost and no power consumption
- Widely used in copper, gold, and iron beneficiation
3. Electro-Magnet

Electro-magnets play a vital role in mineral separation, ensuring precise sorting and removal of metallic contaminants during processing.
- Adjustable magnetic field strength
- Durable and corrosion-resistant design
- Improves equipment longevity and refining quality
4. Wet Pan Mill

The Wet Pan Mill grinds ore into fine particles, preparing it for further concentration and refining. It’s widely used in small and medium mineral processing operations.
- High grinding efficiency and uniform output
- Cost-effective and easy maintenance
- Perfect for mixing and grinding copper ore
ORO Mineral Co., Ltd. — Trusted Partner in Mineral Processing

ORO Mineral Co., Ltd. is a leading manufacturer of mineral processing, screening, and sand washing equipment, established in 2014. Based in China, ORO Mineral specializes in developing advanced solutions for mineral refinement and solid waste recovery.
With a strong R&D foundation and years of experience, ORO Mineral’s equipment has contributed to industries such as mining, metallurgy, construction, and environmental protection.
Our Products Include:
ORO Mineral continues to innovate and refine its technology to deliver sustainable and high-performance equipment that meets global industrial standards.
Summary Table: Copper Refining Process Overview
| Stage | Description | Output |
|---|---|---|
| Mining and Concentration | Extraction and flotation of copper ore | Copper Concentrate (20–30% Cu) |
| Smelting | Melting and separation of impurities | Matte (60–70% Cu) |
| Converting | Oxidation of impurities to produce blister copper | Blister Copper (98–99% Cu) |
| Fire Refining | Removal of residual oxygen and impurities | Anode Copper |
| Electrolytic Refining | Deposition of pure copper via electrolysis | Refined Copper (99.99% Cu) |
FAQs
1. What is the main purpose of copper refining?
The main goal is to remove impurities and achieve high-purity copper suitable for industrial and electrical use.
2. Which is more eco-friendly — pyrometallurgical or hydrometallurgical refining?
Hydrometallurgical refining is more eco-friendly, producing fewer emissions and utilizing less energy.
3. What role does ORO Mineral play in copper refining?
ORO Mineral provides essential mineral processing and separation equipment that enhances refining efficiency and output quality.
4. How pure is refined copper?
Refined copper typically reaches 99.99% purity after electrorefining.
5. What equipment is crucial for refining?
Key equipment includes separators, mills, and electromagnetic systems that ensure efficient mineral processing.